In the universe, unknown power known as dark energy acts everywhere.Dark energy accelerates the universe expansion, and as a result, the galaxies are increasingly faster from each other.But there is one problem.I don't know at all what dark energy is.What does it mean that you don't know about such an important power?
Observatory has been raising the identity of dark energy for decades as an important question.And now, a new space telescope is about to start searching for this challenge.The Euclid Space Telescope, which is launched by the European Space Organization (ESA) in late 2022, is an unprecedented observation device and is sent to the universe to finally elucidate some of the mysteries of dark energy.
At the same time, the observation of the dark matter will be carried out with unprecedented accuracy.Dark Matter is an invisible mysterious substance that exists in the universe, which is much larger than ordinary substances in mass ratio.These observations will make our knowledge of the universe much move forward.
"At this time, there is no persuasive theory about the identity of dark energy," says Katherine Hymann, a professor of space physics at the University of Edinburgh.She is also a Scottish royal astronomer, and also participates in the Euclid Consortium, a 1,500 research group that scrutinizes data collected by Euclid Space Telescapes."What is the cause of the dark energy phenomenon?
Euclid Space Telescope is expected to achieve results following the telescope, such as the ESA Planck Space Telescope.The Planck Space Telescope observed the space microwave background radiation, that is, the remnants of the Big Bang heat from 2009 to 2013.On the other hand, Euclid Space Telescope will observe the universe on infrared and visible lights instead of microwaves.Thus, the Euclid Space Telescope will be able to measure the acceleration of space expansion with dark energy "5 to 10 times better" than ever, says Rene Lawriss, a scientist involved in the project.
Measurement of dark matter by Euclid Space Telescope deepens the understanding of the structure of the universe, which leads to a fundamental verification of various theories."By observing how gravity changes this structure, it is possible to actually verify Einstein's general relativity in the whole universe," says Hymann.
Photograph by Benedict Redgrove
The Euclid Space Telescope Mission has been prepared over 10 years since ESA decided to adopt it in 2011.After the adoption, the contractor started design and manufacture the same telescope.The results were fruited, and in 20 years it was assembled and tested in a clean room of Airbus facilities in Toulose, France.
The Euclid Space Telescope is overall, 4.5m in height, 3.1m in width, and weighs 2,160 kg.The same telescope consists of two parts.It is a servicesmodule that supplies power to the telescope, and a payload module that contains telescope reflector and equipment.
Photograph by Benedict Redgrove
The main components of Euclid Space Telescope are the main mirror contained in the payload modules together with two devices.One of the devices is for shooting the universe with a visible light, and the other is for shooting with near -infrared rays.The main mirror is 1.2 m in diameter, and is observed by combining three reflective mirrors, including this main mirror.This structure is known as a Corsch telescope.
The material of the reflective mirror is silver coated with silver coating.The surface is extremely smooth, so it can detect light from the galaxy far beyond the universe.In order to confirm the accuracy of the main mirror, an optical correction was performed using a flat -plate -type focus reflector (upper photo)."I will use this to position the mirror of the telescope," says Paolo Mushi, a private company in charge of the Euclid Space Telescope Project.
"We are aiming for 2 billion galaxies observation," Lawrace said in a major mission for six years.In other words, it is a pace of observing tens of thousands of galaxies per image.
Scientists study these forms and movements of these galaxies.From the observed form, the distribution of the hidden dark matter that causes these galaxies to be distorted is revealed.The observed movement reveals how fast these galaxies accelerate with dark energy.These observations will be performed on a scale that was not possible before, with the wavelength of visible light and infrared rays.
Shooting a large amount of galaxies with one telescope is the first attempt in history.A 6x6 lattice -shaped charge -shaped element (CCD) is mounted on the same telescope, and the light from the galaxy is captured.
Photograph by Benedict Redgrove
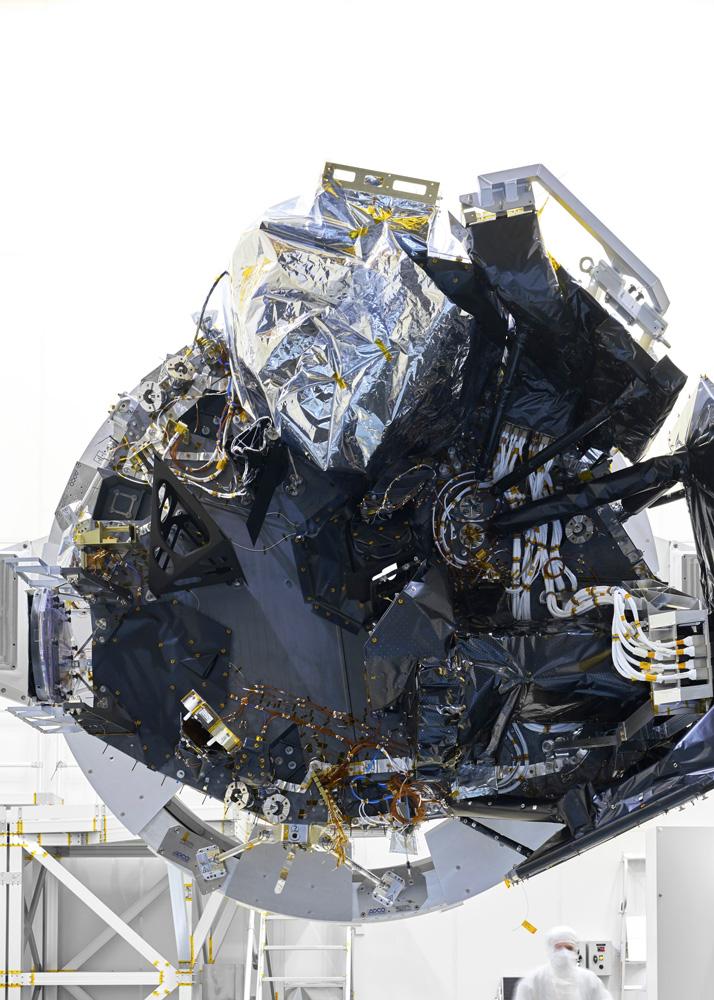
There are two devices in the Payload Module of Euclid Space Telescope.Visible light imaging channels (VIS), near -infrared split metometer and metering meter (NISP).The image quality of the telescope is inferior to the Hubble Space Telescope of the American Aeronautics and Space Bureau launched in 1990.However, Euclid Space Telescope will shoot a large amount of images and reveal a large number of galaxies dating back to the early space.Being able to perform a large amount of observations in this way is a revolutionary point of the same telescope.
"The 3D distribution of the dark matter can be examined about 10 billion years ago," Lawrace says."And, based on the distribution of the galaxy, you can measure the expansion of the universe due to dark energy very accurately."
The Euclid Telescope is launched in space with a Russian Soyuz Rocket.It has been examined to see how components will affect by giving vibration so that they will not break down at the time of launch."The acceleration sensor to measure the vibration source is wired to various devices," Mushi says."It is glued to some parts of the telescope, and monitoring and analyzing the acceleration of each part of the telescope are performed."After these tests in Toulose, the telescope was sent to the Belgian Liese Space Center, and the test was conducted on the heat chamber to ensure that the frozen universe could surely endure the frozen universe.
The Euclid Space Telescope is sent to the second lagrange point (L2) of the sun and the earth, about 1.5 million km from the earth.At this point, the space telescope can stay in a stable trajectory by using a minimum fuel from the combination of the gravity of the sun and the earth.
A thin rectangular sunshade made of carbon fiber enhanced plastic called sunshield protects the side facing the sun of the same telescope.Therefore, light from the sun does not interfere with observation.The same telescope cannot be observed unless it is kept at an extremely low temperature of about -190 ° C.Therefore, the side facing the sunshield of the same telescope is covered with a golden insulation blanket made of Mylar and Carton to keep it low.
Photograph by Benedict Redgrove
The remaining two reflective mirrors other than the Euclid Space Telescope main mirror are for guiding the light collected by the main mirror to two devices, the same telescope, and the same material.The blue object in the photo above is called a dycloic filter and plays a role in dividing light into visible rays and near -infrared wavelengths.Then, a yellow folding mirror guides light.
By all of these, the same telescope will be able to capture the galaxies and their forms accurately."If you want to shoot a form, you must definitely prevent the distortion caused by the shooting equipment," says Gusseeppe Lucka, the director of the project in ESA.。"So the Euclid Space Telescope must be made so perfectly."
Photograph by Benedict Redgrove
Euclid Space Telescope Collected outer observation data is 100 gigabytes per day.Equipment such as VIS (in the above photo, is covered with aluminum foil removed before the launch) will observe such a large amount of data.Such data is sent to the Earth's antenna.Later, it will be sent to various research groups participating in the Euclid Consortium and analyzed."I'm currently trying out how to sort the data," Lawrace says."We are trying to prevent bottlenecks from occurring with this procedure."
The development of the Euclid Space Telescope components began in 2013 after the end of the design work.The assembly itself began in February 2019.By mounting the telescope to the trolley system for several months, various parts were performed while rotating.
"Furthermore, workers wore white dustproof in a special way to prevent pollution from optical equipment," says Mushi."If contamination occurs, noise may be in the image."In 22 years, the telescope was finally mounted on a rocket payload bay, and is ready to be fired from a European launch base in Coolu, French territory.
Various tools and components are used through the Euclid Space Telescope test phase.After that, they are removed and returned to the storage space."You will need a lot of tools during the machine test," Laurent Brouar, the chief of Euclid program on Airbus.For example, there is a component used to fix various parts for the same telescope during work.There is no need to actually launch these components after the completion of the telescope.
The cable mounted on the Euclid Space Telescope may have a rise in temperature and adversely affect images.Therefore, the cable must be far from the same telescope reflector.In addition, there is a possibility that the cable interferes with each other and causes noise in the image.For this reason, an electromagnetic balance test is conducted to confirm that cables do not interfere with each other and have no problems with each other."It is better to have the number of electronic components (in the telescope) as small as possible," says Bruar.The Euclid Space Telescope will acquire the high accuracy needed to advance the understanding of the universe.
Photograph by Benedict Redgrove
In order to keep the Euclid space telescope at low temperature, the radiator plays the role of cooling in outer space after the launch.The heat is removed from the device and the heat is exhausted toward the vacuum.This method is commonly used in other space missions, such as the International Space Station, to prevent the temperature from rising too much over sunlight."There is no air to take the heat," says Mushi."That's why I can only exhaust heat on the principle of radiation."The radiator is connected to the device.This will definitely prevent the delicate mission of observing the galaxy from having heat.
The payload module of Euclid Space Telescope with a reflective mirror and equipment is mounted on a servicesmodge containing electronic components, based on the six -mounted bracket, which is the "leg".One of the brackets can be found in the photo above.The insulation blanket on it protects the side facing the sunshield of the payload module.
Many of the 2 billion galaxies subject to observation can only reach extremely faint light.It is not easy to create an observation device that has enough sensitivity of such a galaxy.However, with Euclid Space Telescope, everything is combined, from extremely accurate reflective mirrors to legs, and is possible."I'm very excited," says High Man."It's a moment that can be said to be the culmination of my career."
